The basic configuration using a transistor is shown in figure bellow. This circuit produces a sine wave low frequency signal in the frequency range between some hertz and some hundreds quilohertz. In the practical applications is recommended make C1 = C2 and R1 = R2.

Formula 1
Frequency:
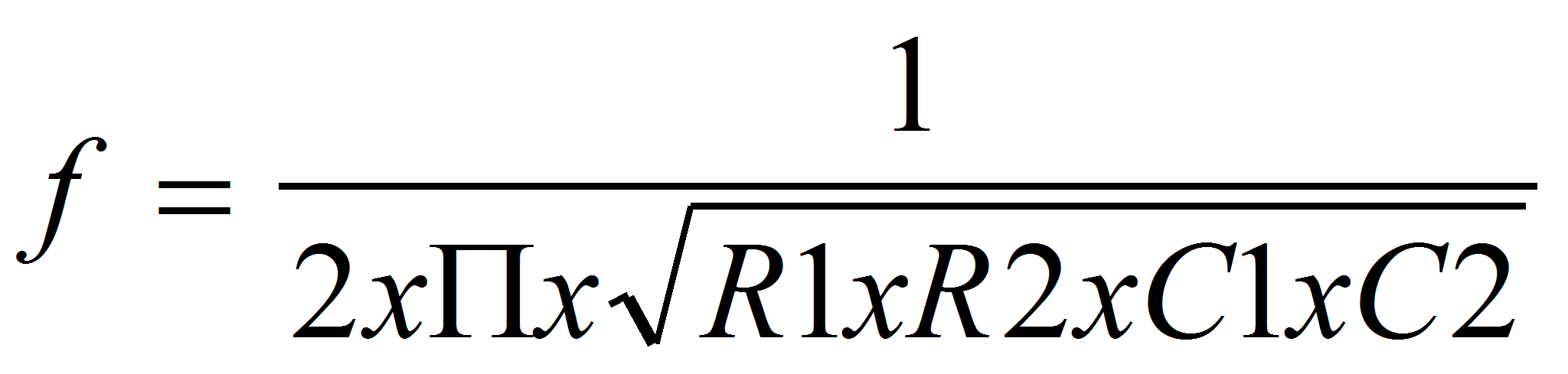
Where:
f is the frequency in hertz (Hz)
R1 and R2 are the resistances in ohm (Ω)
C1 and C2 are the capacitances in farads (F)
π is the constant 3.1415
Application example:
Calculate the frequency of a Wien-Bridge Oscillator where C1 = C2 = 20 nF and R1 = R2 = 20 kΩ.
Data:
R1 = R2 = 20 kΩ
C1 = C2 = 20 nF
Using formula 1:

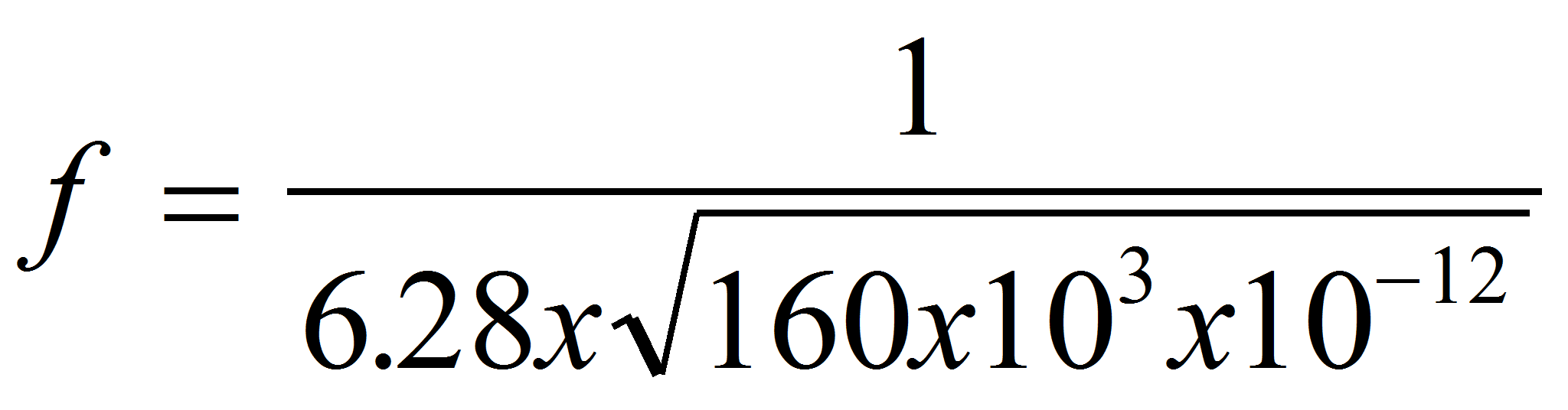
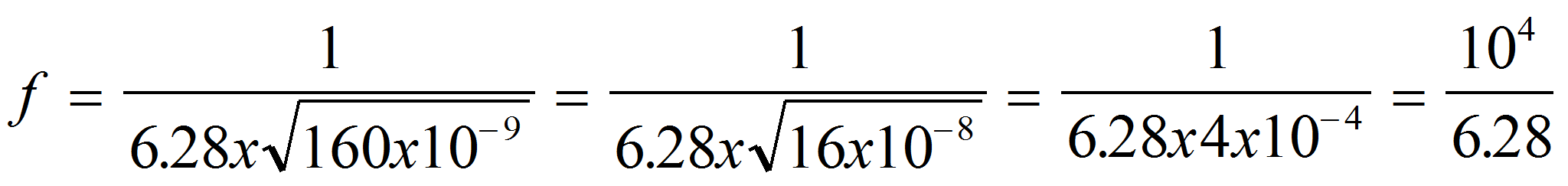
f = 1 592.35 Hz or 1.592 kHz



