Differentiation is a process used to find the instantaneous rate of change of a signal by finding the slope of a line tangent to the point of interest of then graph of the function of the signal. Figure bellow shows a basic differentiation circuit using an operational amplifier.
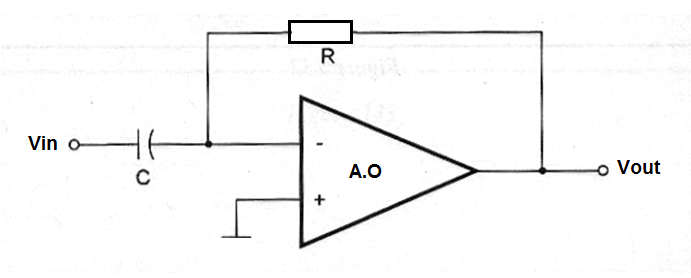
Formula:
Differentiation:
Vout = -R x C x ( dVin / dt)
Where:
Vout is the instantaneous output voltage in volts (V)
Vin is the input voltage in volts (V)
R is the resistance in ohm (Ω)
C is the capacitance in farads (F)



