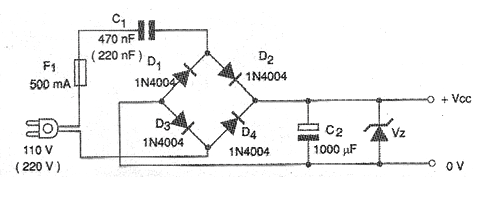
A very simple and useful type of power supply is one that does not use the transformer. Although this component is highly recommended, given the isolation it provides, there are cases in which, due to economy, space limitations or even the lack of such great security, a power supply without a transformer can be used. These sources take advantage of the capacitive reactance of a capacitor, usually high voltage polyester, to reduce the voltage of the power grid.
After that, rectification, filtering and regulation are carried out. Typical transformerless sources are used to power low-consumption devices such as calculators, watches and other similar equipment whose voltage is typically in the 1.5 to 9 V range. The currents required by these devices must not exceed 20 mA. With higher currents, the required capacitors would be very large, in which case the transformer starts to become more interesting. In the figure we have the circuit of a source without a transformer for currents up to 20 mA. The zener diode determines the output voltage.
The polyester capacitor has different values, depending on whether the network is 110 V or 220 V. The values in parentheses are for the voltage of 220 V. Its working voltage must be at least twice the voltage of the network where the circuit is going to be used. It is important to take great care with the insulation of all parts of the device that must be powered and of the source itself, as it is directly connected to the network. No equipment with exposed metal or electrical parts should be powered with this type of source.